Identifying emergence process of group panic buying behavior under the COVID-19 pandemic |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. School of Statistics and Mathematics, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, 310018, China;2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Statistical Data Engineering Technology & Application, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, 310018, China;3. Department of Computer Science and Information Systems, University of North Georgia, Oakwood, GA, 30566, USA;4. School of Tourism and Urban-Rural Planning, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, 310018, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 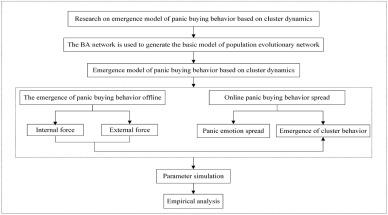
The sudden COVID-19 caused frequent incidents of large-scale material panic buying, resulting in imbalance in supply and demand of goods and threatening social stability. It is of great significance to analyze the formation of group panic buying and help alleviate such action. This paper takes the panic buying phenomenon as the research target, quantifies the internal and external factors affecting individual buying behavior, restores the selection process of individual buying behavior, and constructs the emergence model of group panic buying behavior by using the idea of cluster dynamics. Through simulations, we find that: (1) The epidemic information intensity has a significant impact on the emergence of group rush buying behavior. (2) Government intervention plays a significant role in reducing the scale of group rush buying. Besides, the effects of intervention reach the best before people who do not participate in rush buying disappear. In addition, we also discuss the impact, limitations and future research directions. |
| |
| Keywords: | Panic buying Cluster dynamics Behavior emergence COVID-19 |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

